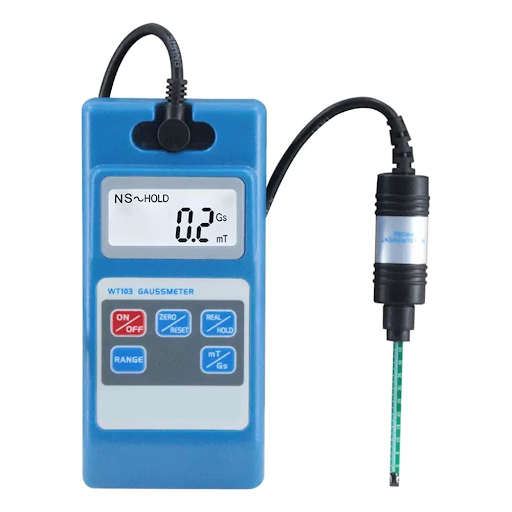
A Gauss meter is a device that measures the strength of electromagnetic fields. It can be used to detect sources of magnetic fields in industry, petrochemical plants, and power utilities. The meter is sensitive to magnetic fields ranging from 1 to 37 Gt. Gauss meters are designed to use low-cost sensors, while still achieving high accuracy
Gauss meters measure the strength of electromagnetic fields
Gauss meters measure the strength of electromagnetic fields. They are used in industry, petrochemical plants, and power utilities to detect electric and magnetic fields. Gauss meters are designed to use low-cost sensors that can be easily integrated into existing systems or replaced with a new sensor if needed. They are accurate because they use sophisticated mathematical calculations based on principles developed by Hans Christian Oersted (1804), who first discovered that electric currents produce magnetic effects when they pass through materials such as wire coils or solids with magnets attached.
Analog meters measure either AC or DC voltages, while digital meters do both
- Analog meters are cheaper and have an easier time reading voltages below 0.1V.
- Digital multimeters can be used to test batteries, resistors and capacitors, transistors, and integrated circuits (ICs).
Digital gauss meters are more expensive, but they are much easier to use. They can be used to measure voltage, current, and resistance without the need for additional equipment. The digital multimeter is also more accurate than an analog one, giving you an exact number rather than just a range of values in which your reading falls.
The meter is sensitive to magnetic fields ranging from 1 to 37 giga-Tesla (Gt)
The Gauss meter is used to measure magnetic fields ranging from 1 to 37 Gt. Gauss meters are also known as GM (Giga-Tesla) or T-magnitude meters, and they are sensitive to magnetic fields in the range of 0.1 to 10 mT. The main application for these devices is industrial quality control and process control, where they can be used for measuring electrical currents caused by motors, generators, transformers, and other machinery that generate high voltages on the power grid.
Gauss meters are designed with low-cost sensors, while still achieving high-accuracy readings when compared with expensive reference standards such as HVAC units or fuses.
Uses of Gauss Meter
Gauss meters are used for measuring magnetic fields in industry, petrochemical plants, and power utilities. A Gauss meter is a device that measures the strength of electromagnetic fields. It’s used to detect when an object has been moved into an area where it shouldn’t be—for example, if you’re working near a sensitive piece of equipment and need to know when someone walks past you.
The most common type of Gauss meter consists of two coils: one produces a current while the other senses how much current flows through it (this is called “field intensity”). The difference between these two measurements can give you information about what’s happening inside or outside your field–and help identify whether any unauthorized individuals might be entering it!
Gauss meters are designed to use low-cost sensors, while still achieving high accuracy
Gauss meters are designed to use low-cost sensors, while still achieving high accuracy. Gauss meters have been used in industry, petrochemical plants, and power utilities for decades. The technology has improved over time but remains very accurate even when using inexpensive sensors such as those found in consumer electronics like smartphones or wearables.
Gauss meters can be used in many applications such as:
- Industrial metrology – Measuring the properties of metal alloys and other material types with an accuracy of 0.1% (10 parts per million) or better;
- Environment monitoring – Measuring biological activity at a site where contamination may exist;
- Power quality measurement – Detecting voltage disturbances within electric power lines so that they can be eliminated before damage occurs;
A Gauss meter is a device that measures the strength of electromagnetic fields
Gauss meters are devices that measure the strength of electromagnetic fields. They are used to measure magnetic fields in industry, petrochemical plants, and power utilities.
They can also be used to measure the strength of other types of fields, such as radio waves and microwaves.
Gauss meters are useful for measuring the strength of magnetic fields. They can be used in industrial settings, which is why they have become popular tools for engineers and scientists. In this article we’ve explored how these devices work, along with some tips on how you might use one yourself—it’s always a good idea to learn more about any new products or services before using them!